Introduction
This page presents how TINA.sift do cope efficiently with the StateSpace examination face to the other participating tools. In this page, we consider «Stripped» models.
The next sections will show chart comparing performances in termsof both memory and execution time.The x-axis corresponds to the challenging tool where the y-axes represents TINA.sift' performances. Thus, points below the diagonal of a chart denote comparisons favorables to the tool whileothers corresponds to situations where the challenging tool performs better.
You might also find plots out of the range that denote the case were at least one tool could not answer appropriately (error, time-out, could not compute or did not competed).
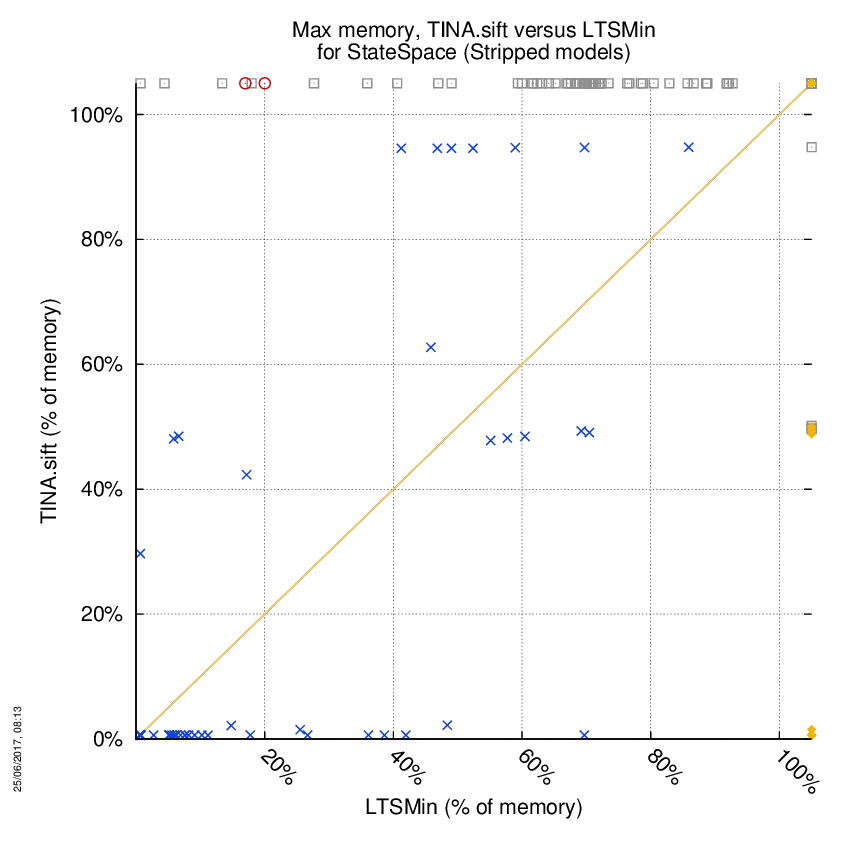
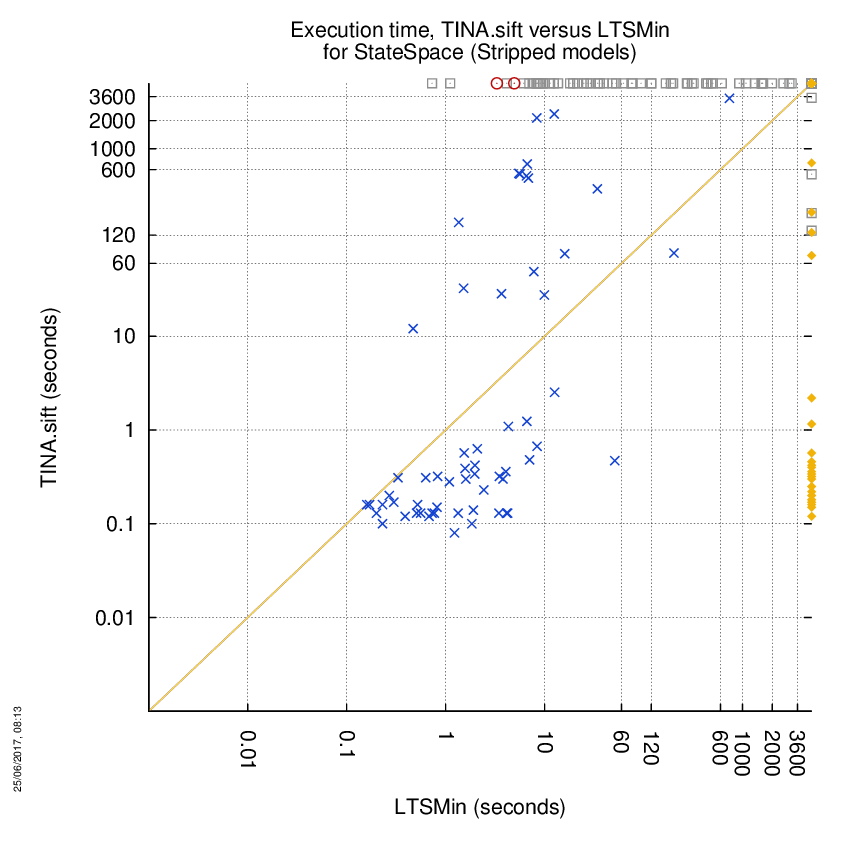
TINA.sift versus LTSMin
Some statistics are displayed below, based on 866 runs (433 for TINA.sift and 433 for LTSMin, so there are 433 plots on each of the two charts). Each execution was allowed 1 hour and 16 GByte of memory. Then performance charts comparing TINA.sift to LTSMin are shown (you may click on one graph to enlarge it).
| Statistics on the execution | ||||||
| TINA.sift | LTSMin | Both tools | TINA.sift | LTSMin | ||
| Computed OK | 26 | 56 | 59 | Smallest Memory Footprint | ||
| Do not compete | 0 | 120 | 0 | Times tool wins | 73 | 68 |
| Error detected | 2 | 0 | 0 | Shortest Execution Time | ||
| Cannot Compute + Time-out | 152 | 4 | 194 | Times tool wins | 69 | 72 |
On the chart below, ![]() denote cases where
the two tools did computed a result without error,
denote cases where
the two tools did computed a result without error, ![]() denote the cases where at least one tool did not competed,
denote the cases where at least one tool did not competed,
![]() denote the cases where at least one
tool computed a bad value and
denote the cases where at least one
tool computed a bad value and ![]() denote the cases where at least one tool stated it could not compute a result or timed-out.
denote the cases where at least one tool stated it could not compute a result or timed-out.
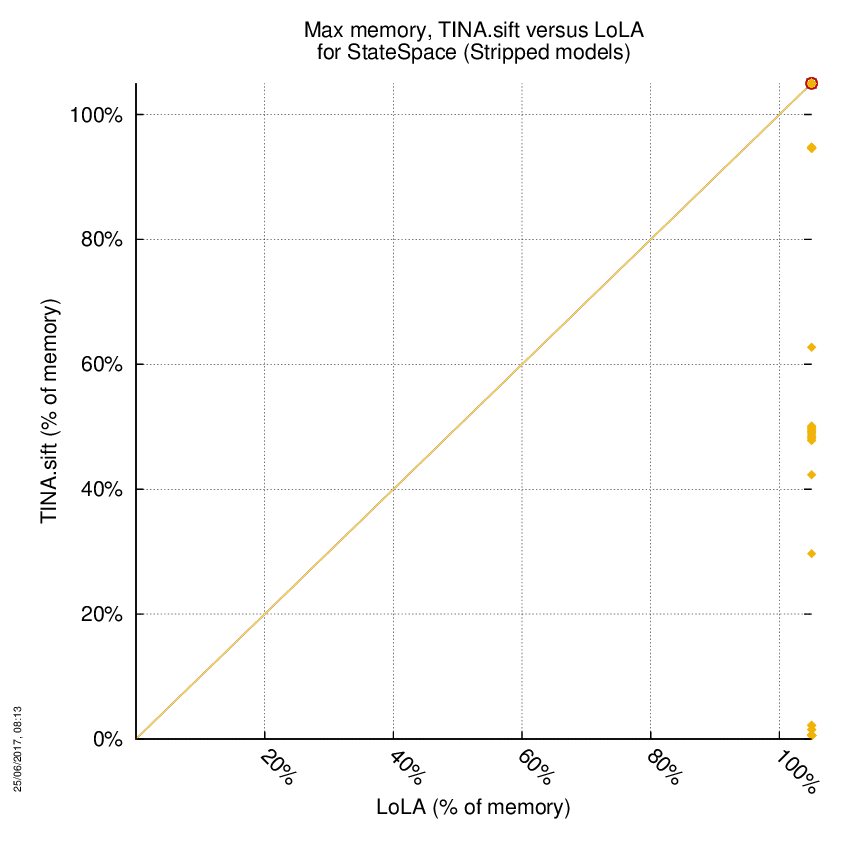
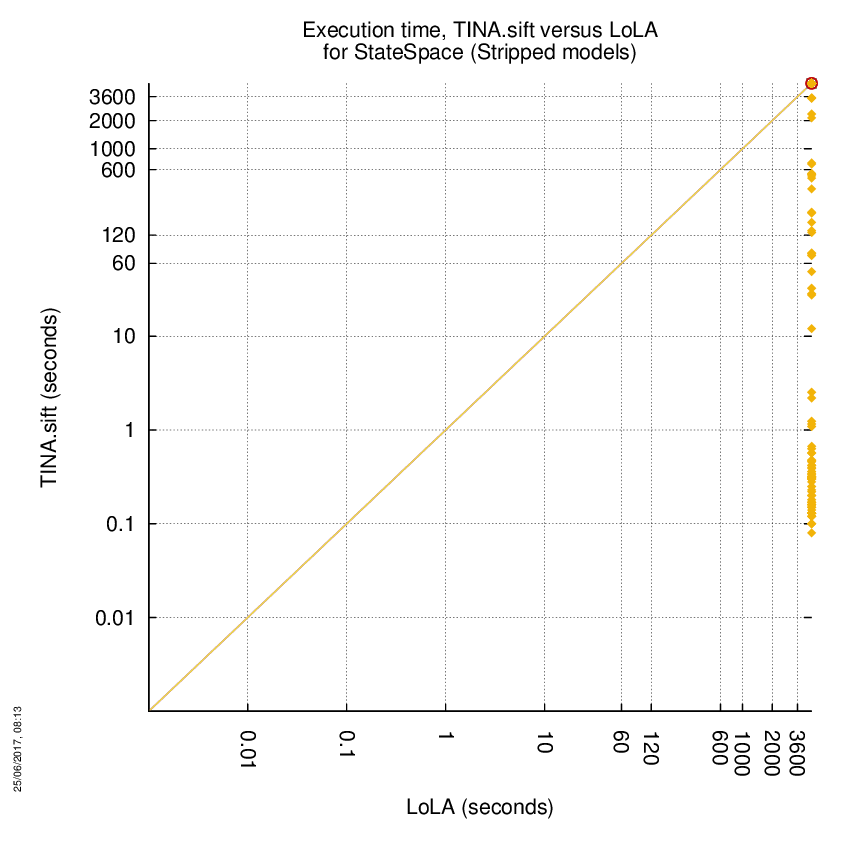
TINA.sift versus LoLA
Some statistics are displayed below, based on 866 runs (433 for TINA.sift and 433 for LoLA, so there are 433 plots on each of the two charts). Each execution was allowed 1 hour and 16 GByte of memory. Then performance charts comparing TINA.sift to LoLA are shown (you may click on one graph to enlarge it).
| Statistics on the execution | ||||||
| TINA.sift | LoLA | Both tools | TINA.sift | LoLA | ||
| Computed OK | 85 | 0 | 0 | Smallest Memory Footprint | ||
| Do not compete | 0 | 423 | 0 | Times tool wins | 85 | 0 |
| Error detected | 2 | 0 | 0 | Shortest Execution Time | ||
| Cannot Compute + Time-out | 336 | 0 | 10 | Times tool wins | 85 | 0 |
On the chart below, ![]() denote cases where
the two tools did computed a result without error,
denote cases where
the two tools did computed a result without error, ![]() denote the cases where at least one tool did not competed,
denote the cases where at least one tool did not competed,
![]() denote the cases where at least one
tool computed a bad value and
denote the cases where at least one
tool computed a bad value and ![]() denote the cases where at least one tool stated it could not compute a result or timed-out.
denote the cases where at least one tool stated it could not compute a result or timed-out.
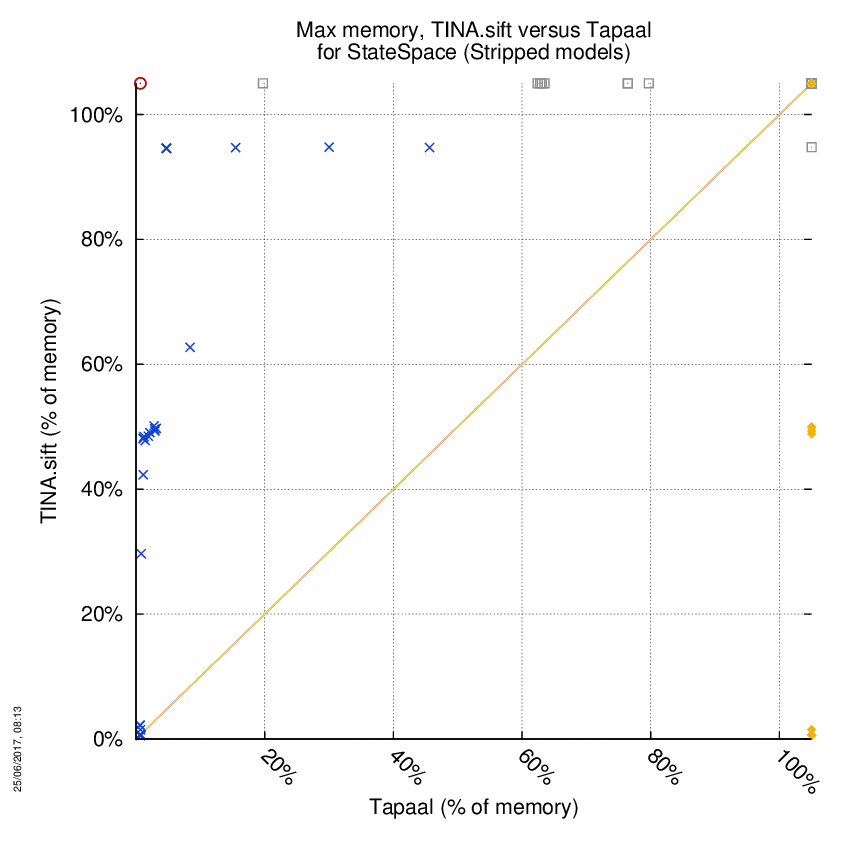
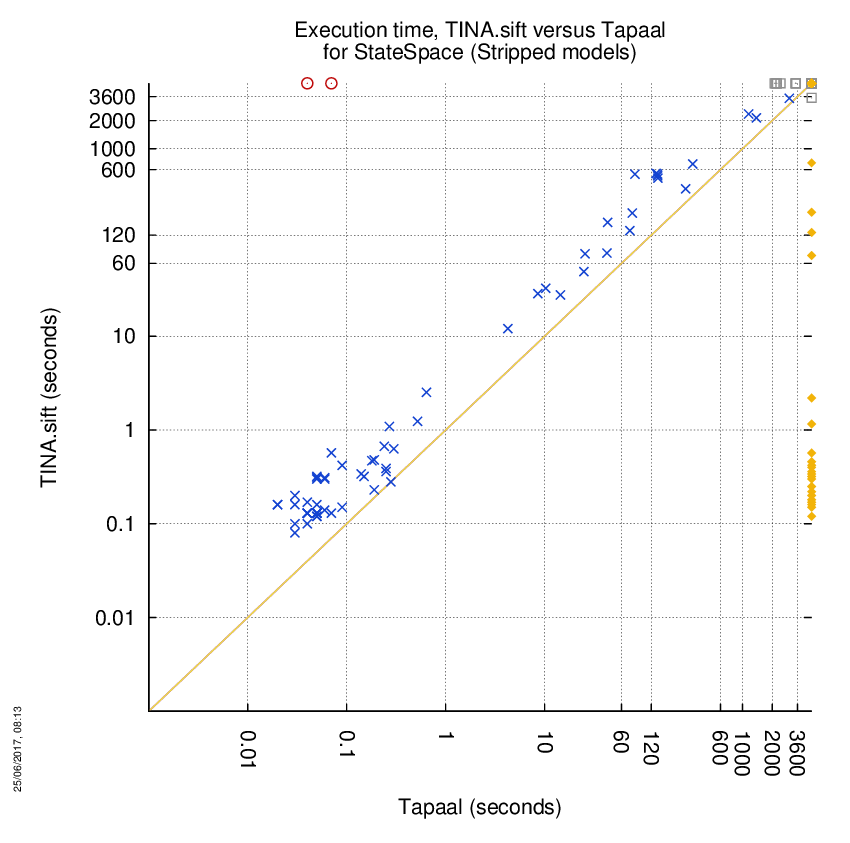
TINA.sift versus Tapaal
Some statistics are displayed below, based on 866 runs (433 for TINA.sift and 433 for Tapaal, so there are 433 plots on each of the two charts). Each execution was allowed 1 hour and 16 GByte of memory. Then performance charts comparing TINA.sift to Tapaal are shown (you may click on one graph to enlarge it).
| Statistics on the execution | ||||||
| TINA.sift | Tapaal | Both tools | TINA.sift | Tapaal | ||
| Computed OK | 23 | 10 | 62 | Smallest Memory Footprint | ||
| Do not compete | 0 | 120 | 0 | Times tool wins | 62 | 33 |
| Error detected | 2 | 0 | 0 | Shortest Execution Time | ||
| Cannot Compute + Time-out | 106 | 1 | 240 | Times tool wins | 23 | 72 |
On the chart below, ![]() denote cases where
the two tools did computed a result without error,
denote cases where
the two tools did computed a result without error, ![]() denote the cases where at least one tool did not competed,
denote the cases where at least one tool did not competed,
![]() denote the cases where at least one
tool computed a bad value and
denote the cases where at least one
tool computed a bad value and ![]() denote the cases where at least one tool stated it could not compute a result or timed-out.
denote the cases where at least one tool stated it could not compute a result or timed-out.
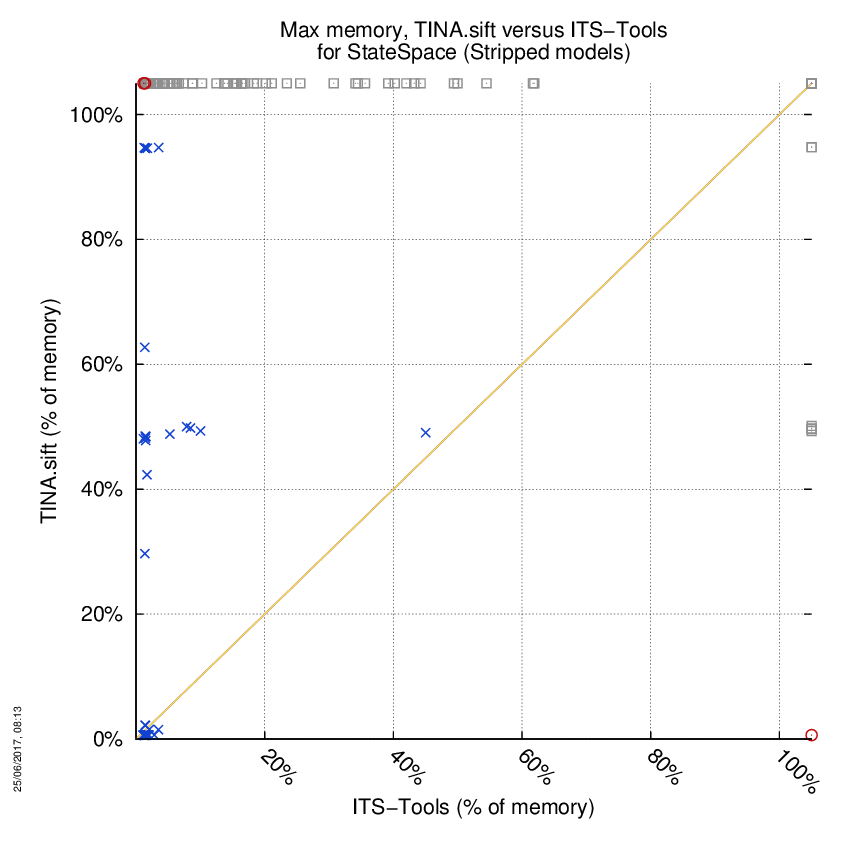
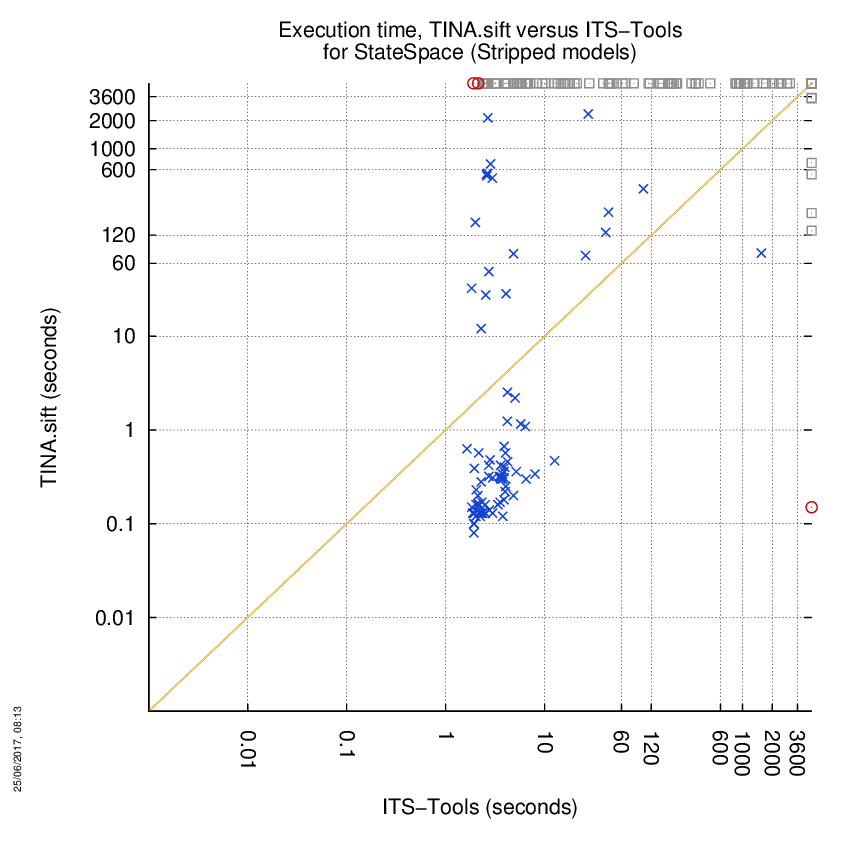
TINA.sift versus ITS-Tools
Some statistics are displayed below, based on 866 runs (433 for TINA.sift and 433 for ITS-Tools, so there are 433 plots on each of the two charts). Each execution was allowed 1 hour and 16 GByte of memory. Then performance charts comparing TINA.sift to ITS-Tools are shown (you may click on one graph to enlarge it).
| Statistics on the execution | ||||||
| TINA.sift | ITS-Tools | Both tools | TINA.sift | ITS-Tools | ||
| Computed OK | 7 | 86 | 78 | Smallest Memory Footprint | ||
| Do not compete | 0 | 0 | 0 | Times tool wins | 64 | 107 |
| Error detected | 2 | 1 | 0 | Shortest Execution Time | ||
| Cannot Compute + Time-out | 84 | 6 | 262 | Times tool wins | 67 | 104 |
On the chart below, ![]() denote cases where
the two tools did computed a result without error,
denote cases where
the two tools did computed a result without error, ![]() denote the cases where at least one tool did not competed,
denote the cases where at least one tool did not competed,
![]() denote the cases where at least one
tool computed a bad value and
denote the cases where at least one
tool computed a bad value and ![]() denote the cases where at least one tool stated it could not compute a result or timed-out.
denote the cases where at least one tool stated it could not compute a result or timed-out.
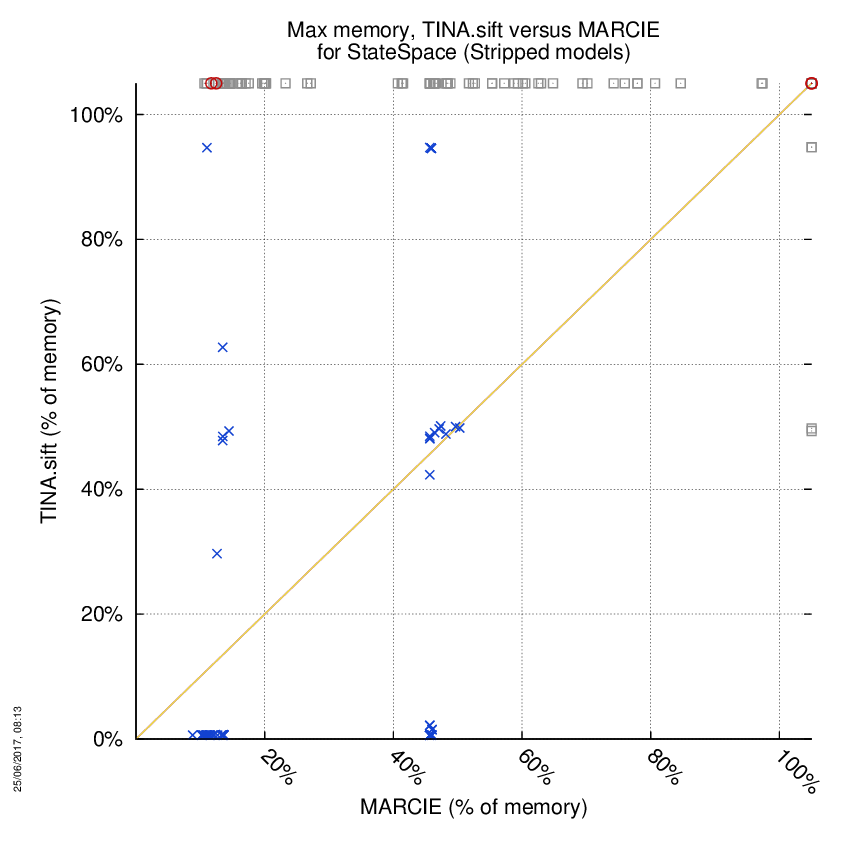
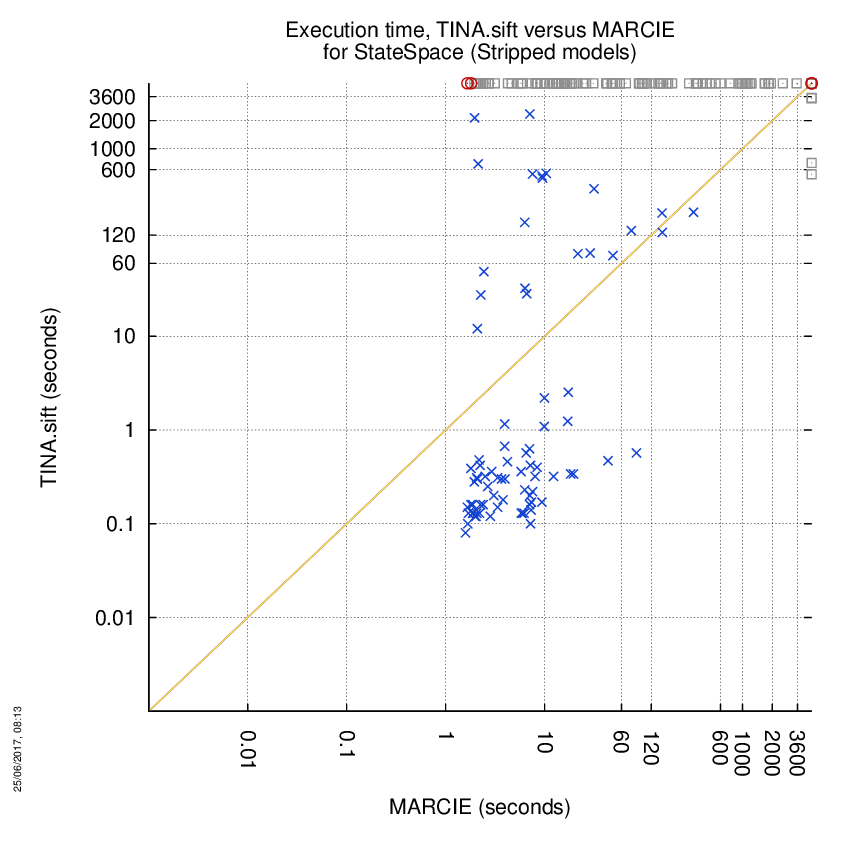
TINA.sift versus MARCIE
Some statistics are displayed below, based on 866 runs (433 for TINA.sift and 433 for MARCIE, so there are 433 plots on each of the two charts). Each execution was allowed 1 hour and 16 GByte of memory. Then performance charts comparing TINA.sift to MARCIE are shown (you may click on one graph to enlarge it).
| Statistics on the execution | ||||||
| TINA.sift | MARCIE | Both tools | TINA.sift | MARCIE | ||
| Computed OK | 4 | 91 | 81 | Smallest Memory Footprint | ||
| Do not compete | 0 | 0 | 0 | Times tool wins | 66 | 110 |
| Error detected | 2 | 2 | 0 | Shortest Execution Time | ||
| Cannot Compute + Time-out | 91 | 4 | 255 | Times tool wins | 66 | 110 |
On the chart below, ![]() denote cases where
the two tools did computed a result without error,
denote cases where
the two tools did computed a result without error, ![]() denote the cases where at least one tool did not competed,
denote the cases where at least one tool did not competed,
![]() denote the cases where at least one
tool computed a bad value and
denote the cases where at least one
tool computed a bad value and ![]() denote the cases where at least one tool stated it could not compute a result or timed-out.
denote the cases where at least one tool stated it could not compute a result or timed-out.
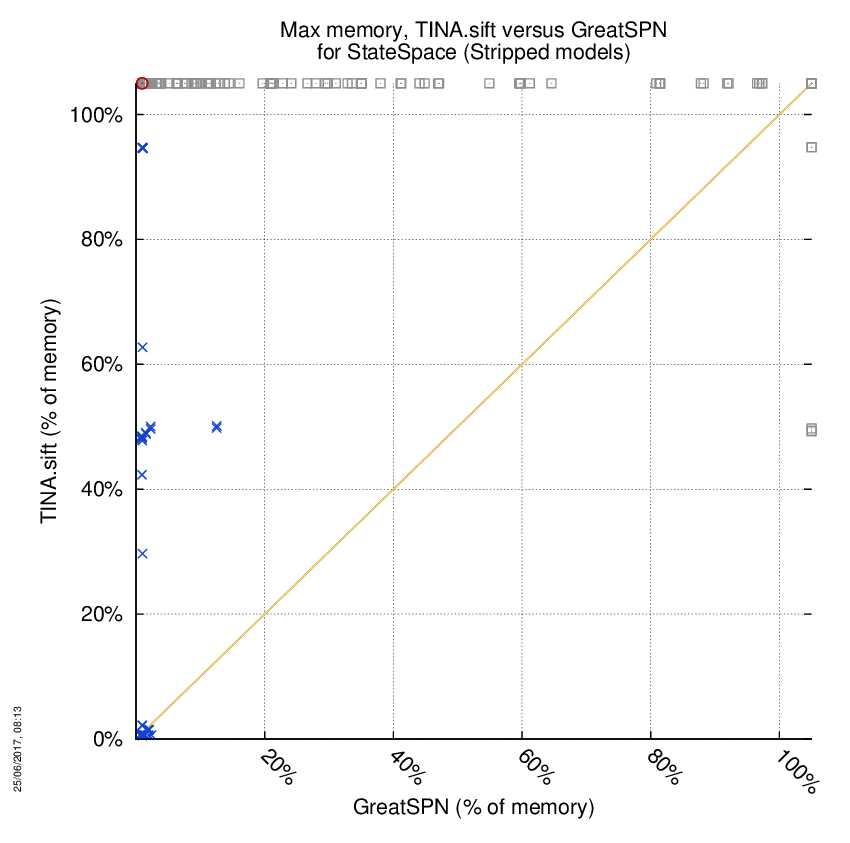
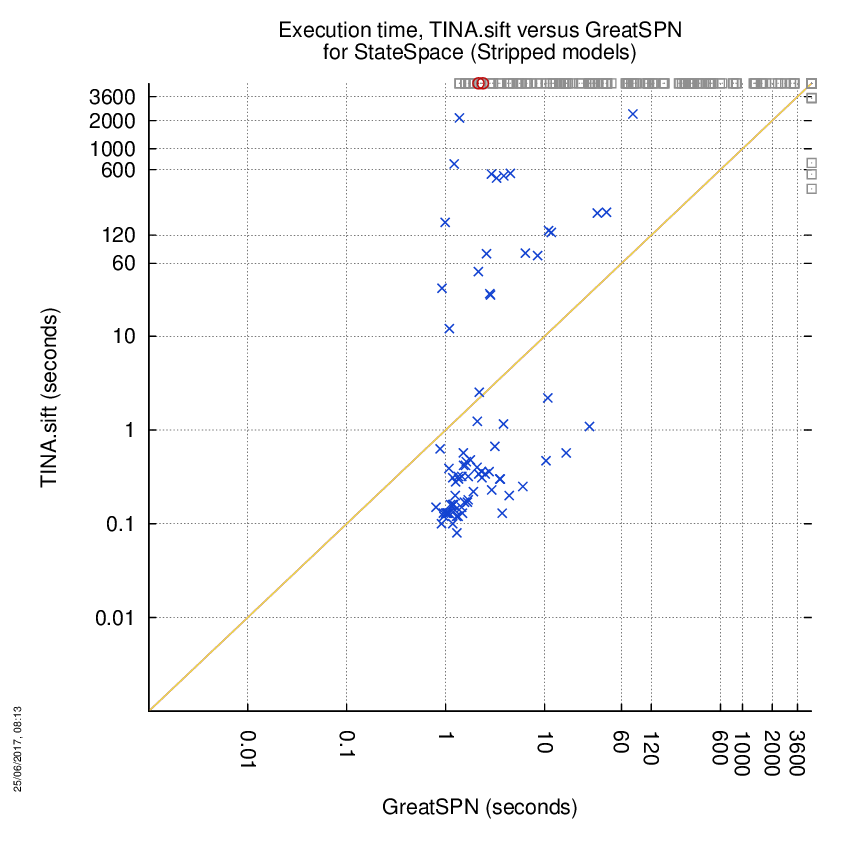
TINA.sift versus GreatSPN
Some statistics are displayed below, based on 866 runs (433 for TINA.sift and 433 for GreatSPN, so there are 433 plots on each of the two charts). Each execution was allowed 1 hour and 16 GByte of memory. Then performance charts comparing TINA.sift to GreatSPN are shown (you may click on one graph to enlarge it).
| Statistics on the execution | ||||||
| TINA.sift | GreatSPN | Both tools | TINA.sift | GreatSPN | ||
| Computed OK | 5 | 124 | 80 | Smallest Memory Footprint | ||
| Do not compete | 0 | 0 | 0 | Times tool wins | 63 | 146 |
| Error detected | 2 | 0 | 0 | Shortest Execution Time | ||
| Cannot Compute + Time-out | 122 | 5 | 224 | Times tool wins | 64 | 145 |
On the chart below, ![]() denote cases where
the two tools did computed a result without error,
denote cases where
the two tools did computed a result without error, ![]() denote the cases where at least one tool did not competed,
denote the cases where at least one tool did not competed,
![]() denote the cases where at least one
tool computed a bad value and
denote the cases where at least one
tool computed a bad value and ![]() denote the cases where at least one tool stated it could not compute a result or timed-out.
denote the cases where at least one tool stated it could not compute a result or timed-out.
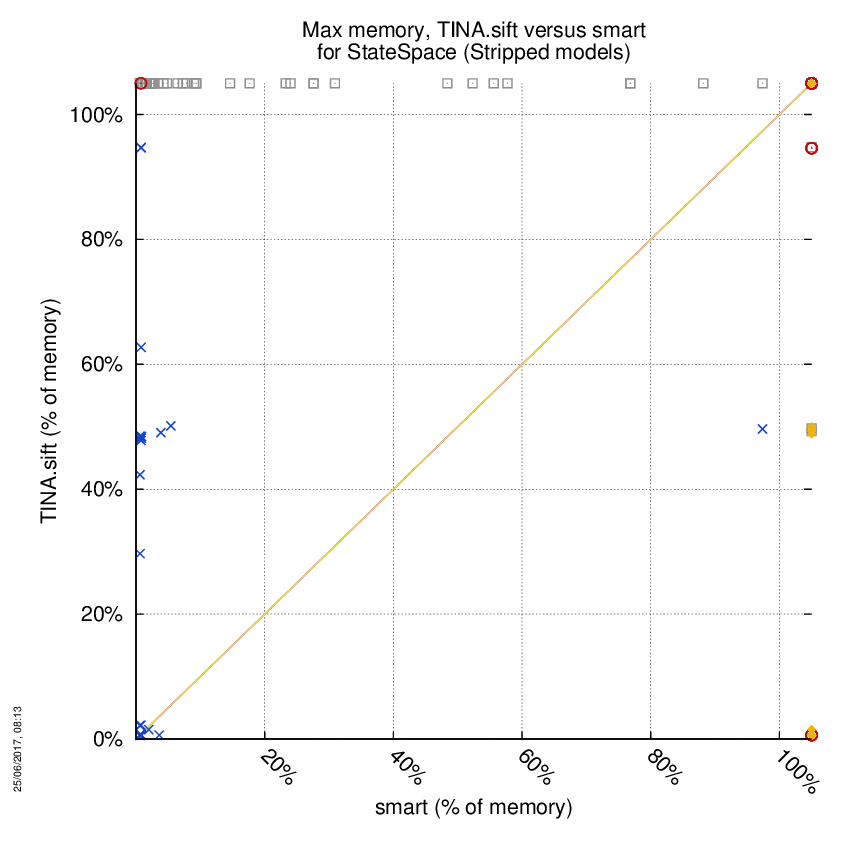
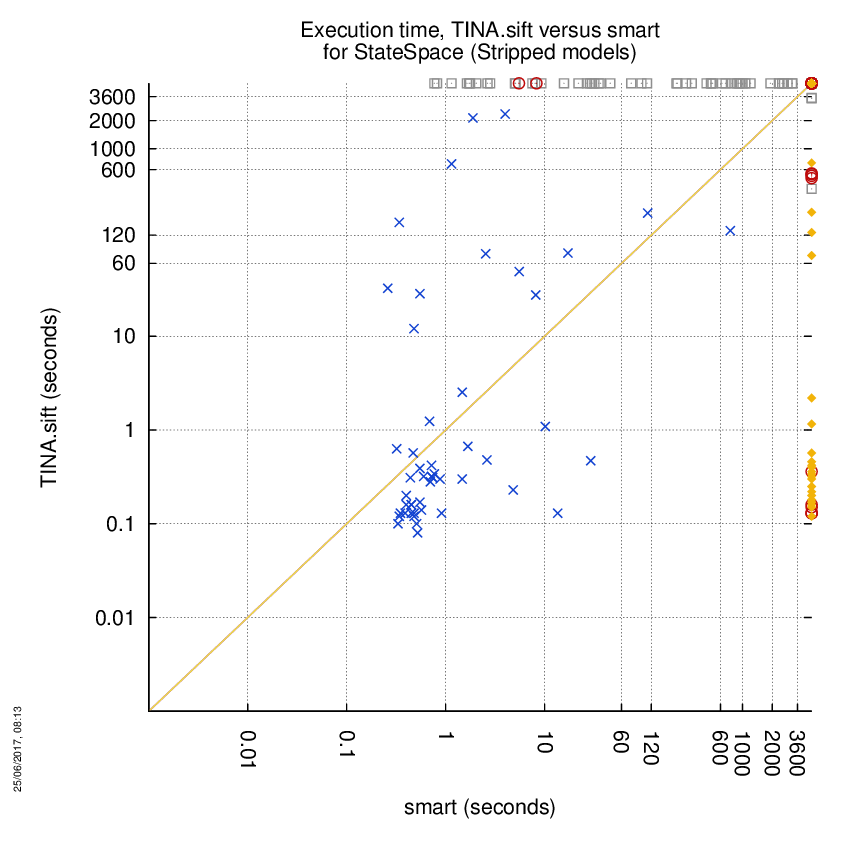
TINA.sift versus smart
Some statistics are displayed below, based on 866 runs (433 for TINA.sift and 433 for smart, so there are 433 plots on each of the two charts). Each execution was allowed 1 hour and 16 GByte of memory. Then performance charts comparing TINA.sift to smart are shown (you may click on one graph to enlarge it).
| Statistics on the execution | ||||||
| TINA.sift | smart | Both tools | TINA.sift | smart | ||
| Computed OK | 36 | 53 | 49 | Smallest Memory Footprint | ||
| Do not compete | 0 | 120 | 0 | Times tool wins | 58 | 80 |
| Error detected | 2 | 21 | 0 | Shortest Execution Time | ||
| Cannot Compute + Time-out | 160 | 4 | 186 | Times tool wins | 69 | 69 |
On the chart below, ![]() denote cases where
the two tools did computed a result without error,
denote cases where
the two tools did computed a result without error, ![]() denote the cases where at least one tool did not competed,
denote the cases where at least one tool did not competed,
![]() denote the cases where at least one
tool computed a bad value and
denote the cases where at least one
tool computed a bad value and ![]() denote the cases where at least one tool stated it could not compute a result or timed-out.
denote the cases where at least one tool stated it could not compute a result or timed-out.
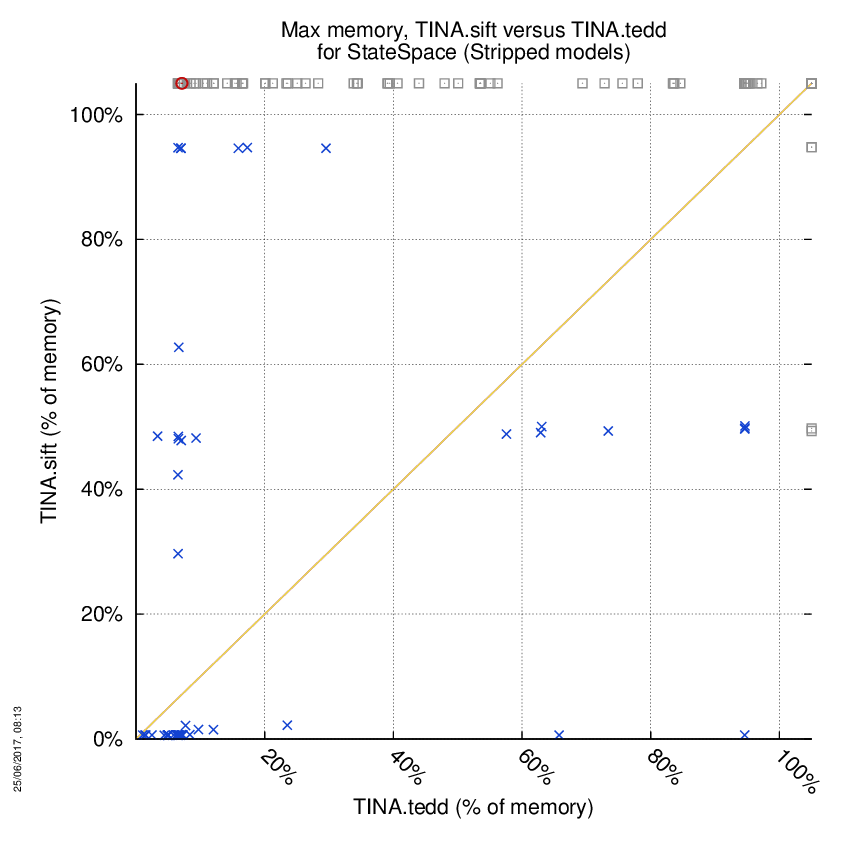
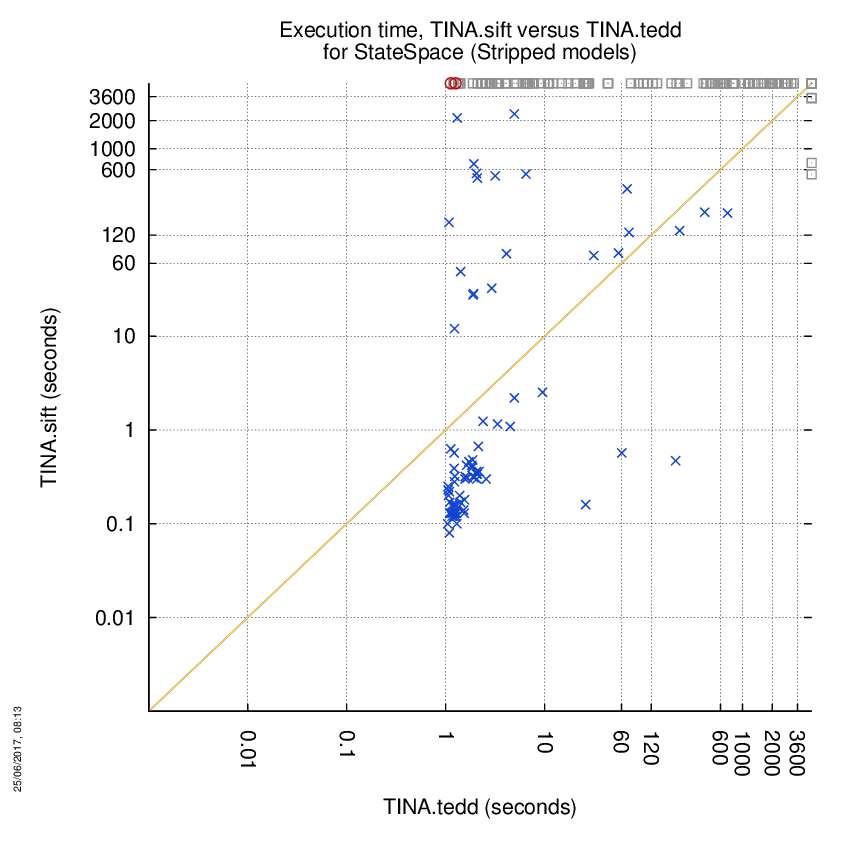
TINA.sift versus TINA.tedd
Some statistics are displayed below, based on 866 runs (433 for TINA.sift and 433 for TINA.tedd, so there are 433 plots on each of the two charts). Each execution was allowed 1 hour and 16 GByte of memory. Then performance charts comparing TINA.sift to TINA.tedd are shown (you may click on one graph to enlarge it).
| Statistics on the execution | ||||||
| TINA.sift | TINA.tedd | Both tools | TINA.sift | TINA.tedd | ||
| Computed OK | 4 | 101 | 81 | Smallest Memory Footprint | ||
| Do not compete | 0 | 0 | 0 | Times tool wins | 71 | 115 |
| Error detected | 2 | 0 | 0 | Shortest Execution Time | ||
| Cannot Compute + Time-out | 99 | 4 | 247 | Times tool wins | 67 | 119 |
On the chart below, ![]() denote cases where
the two tools did computed a result without error,
denote cases where
the two tools did computed a result without error, ![]() denote the cases where at least one tool did not competed,
denote the cases where at least one tool did not competed,
![]() denote the cases where at least one
tool computed a bad value and
denote the cases where at least one
tool computed a bad value and ![]() denote the cases where at least one tool stated it could not compute a result or timed-out.
denote the cases where at least one tool stated it could not compute a result or timed-out.